The latest keto craze on everyone’s lips is collagen peptides. The use of collagen in various beauty and food items is nothing new, but today it seems these essential amino acids have gone viral. This is not surprising considering the health benefits collagen provides, but how much do you really know about it? And more importantly, how do collagen supplements benefit keto dieters? Here is what you need to know.
What Is Collagen?
Collagen is the most abundant form of protein found in both the human and animal anatomy that is quite literally the glue that holds our bodies together. It’s distinctive amino acid profile and glue producing abilities help to form the connective tissue in every square foot of our bodies, from the bones and muscles to the skin. The properties of this protein are so powerful, the world’s oldest glue contained collagen, which was used as an adhesive for bows and to hold utensils together by Ancient Egyptians and Native Americans thousands of years ago.
The main function of collagen is to build and strengthen structures within the body, basically, collagen is the body’s scaffolding, but that is not the only thing we need this unique cement for. Collagen also acts as a defense against harmful elements. It prevents the skin from absorbing pathogenic substances, cancerous cells, microbes, and environmental toxins.
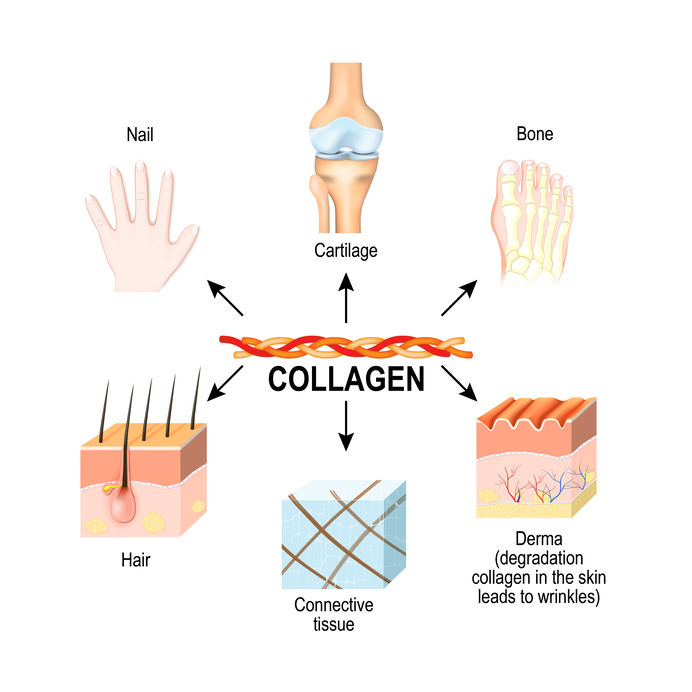
The specific amino acids found in collagen, which are Hydroxyproline, Proline, Glycine, and Arginine to name a few make up almost 30% of the whole-body protein content. For example:
- The bones are made up of 30% collagen (by dry weight)
- The tendons are made up of 80% collagen (by dry weight)
- The sclera or white part of the eye is made up of 90% collagen (by dry weight)
- Cartilage is made up of 60% collagen (by dry weight)
- Muscle mass is made up of 1 to 10% collagen (by dry weight)
In other words, most of the connective tissues found in the body contain a high content of various types of collagen.
The Different Types Of Collagen

As of 2011 over 28 types of collagen have been identified in the body, but types I, II, and III are the most common and abundant.
- Collagen type I, which is the most abundant form of protein found in the teeth, connective tissue, tendons, skin, bones, and cartilage is extremely resilient and can withstand high-pressure conditions without breaking thanks to its molecular structure. Collagen fibers are coiled and intertwined around each other to form fibrillar bundles, which is how collagen gains its tensile strength. These fibrillar bundles carry a hefty tensile strength of 500 to 1000 kg/cm2 which is stronger than steel.
- Collagen type II makes up the main collagenous components of the cartilage and is important for building and maintaining the structural integrity of the joints. Some studies suggest that taking this specific form of collagen can help alleviate pain and inflammation associated with osteoarthritis and other joint disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis.
- Collagen type III is normally found where collagen type I is present, which is in the arteries, muscles, organs, and reticular fiber (a fine mesh-like connective tissue found in the spleen, bone marrow, and liver). Research has linked collagen type III deficiencies to cerebral aneurysms, vascular fragility, and bowel ruptures.
- Collagen type IV is found in the basal lamina – a thin layer of the extracellular matrix that is secreted by epithelial cells and provides the skin cells with support.
- Collagen type V is found in the interstitial matrix, which is the connective tissue located between cells of the lungs, placenta, liver, and muscles. Type V is also found in the cornea and bone matrix.
- Collagen type X is directly involved in the endochondral ossification process, which is the formation of bones during the fetal development in both humans and animals. Type X also plays a crucial role in the repair of broken bones as well as the diarthrosis (The joint that connects the bones in your spine, fingers, toes, and knees together).
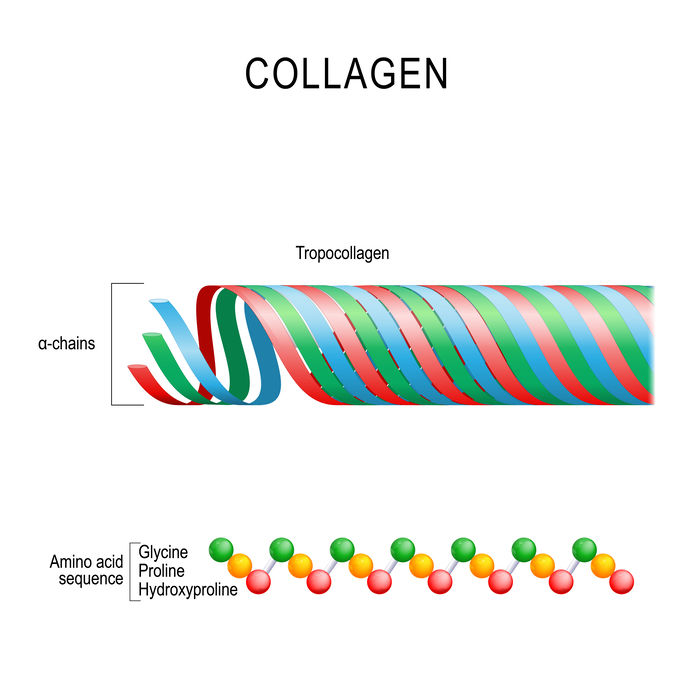
What makes these types of collagen so different in the way they function and where they are located is due to their unique amino acid profile. Our bodies are able to make collagen from the protein and vitamin C in our diets. However, as we age, the body doesn’t produce as much collagen as it would in our younger years. This decline usually begins in our mid-thirties, which as a result causes our skin to wrinkle and increase our chances of fracturing a bone or developing osteoporosis. This is the main reason why many nutritionists suggest eating collagen-rich foods or taking hydrolyzed collagen supplements.
What Is Hydrolyzed Collagen?
Hydrolyzed collagen, also known as collagen peptides, is the type of collagen found in supplement form. This is the type of collagen keto dieters can’t get enough of. The supplements are made by hydrolyzing the molecular bonds that make up collagen, which is usually sourced from the connective tissue and bones of mammals and fish. After the bonds have been hydrolyzed or broken down, they are left to dry and then pulverized into a powder, which is then capsulated or sold in its powder form. This intricate process makes the exogenous collagen more bioactive and soluble in cold water. The purpose of this supplement is to deliver a quick and convenient form of collagen that the body can rapidly digest and utilize. Thanks to collagen peptides, keto dieters have a more convenient way to reach their daily macros and get a quick boost of energy after a workout.
Science-Based Benefits Of Hydrolyzed Collagen
According to research, getting an adequate intake of collagen can offer a wide range of benefits that you can see and feel. From the joints to the skin, collagen has a major effect on your appearance and quality of life. These are a few science-backed benefits of collagen peptides:
Improves Skin Health
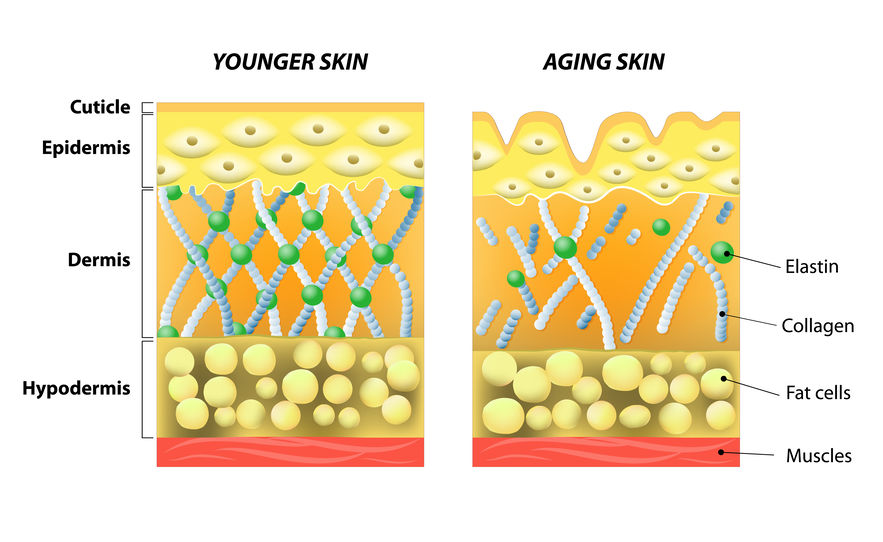
If you live on planet earth, there is no doubt that you have heard about the amazing skin-healing benefits that collagen can provide. It is one of the most widely advertised ingredients in skincare products and all the science is there to back it up. The fibrous protein makes up almost 70% of the dermal volume and is responsible for giving skin its suppleness, firmness, and aids in retaining moisture.
Studies have shown that taking collagen peptides can help reduce wrinkles, skin dryness, and slow down aging. In one study, participants who took 2.5 to 5 grams of hydrolyzed collagen for a period of eight weeks experienced an increase in skin elasticity and a reduction in skin dryness compared to their counterparts who did not take the supplement. In another study, participants who ingested the supplements mixed into a beverage over 12 weeks experienced similar results to the previous study. Results showed that there was a significant reduction in wrinkles and an increase in hydration compared to their counterparts.
Research also suggests that taking exogenous collagen may stimulate the production of proteins that are also involved in providing structure to the skin like fibrillin and elastin.
Preserves Heart Health
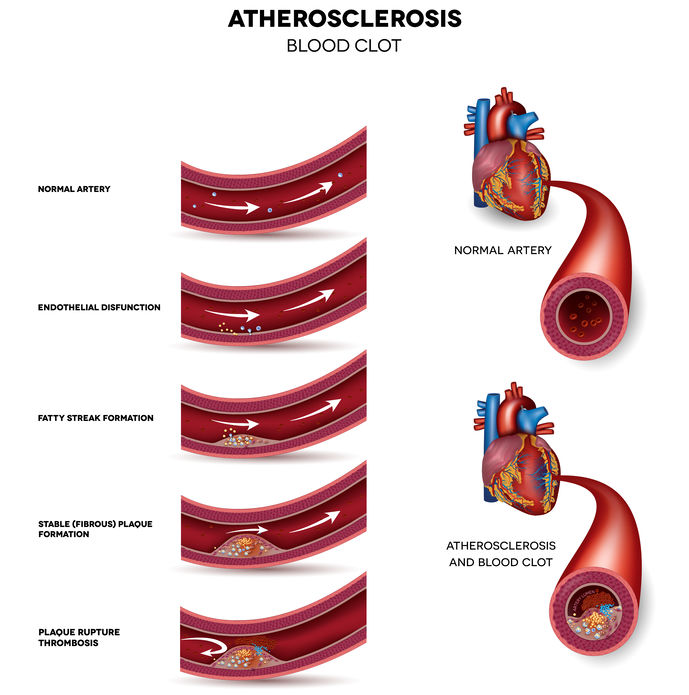
As the body’s main scaffolding, collagen is responsible for the tubular structure that forms our arteries, the tubes that carry blood vessels from our heart to the rest of our body. Without the support that collagen provides, arteries can become fragile and weaken over time. This can lead to several disorders such as atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, which can end in a heart attack or stroke. Researchers believe that taking collagen peptides can reduce the risk of developing cardiovascular disorders. One study, in particular, revealed that participants who had taken collagen supplements every day over six months experienced a decrease in artery stiffness.
Collagen peptides have also shown promise in increasing HDL cholesterol levels by almost 6%. HDL is the “good kind” of cholesterol that helps reduce the risk of heart-related disorders.
Improves Joint Pain
As we age, the amount of collagen our bodies are able to produce starts to cascade, which increases the risk of developing degenerative joint disorders. Researchers have suggested that taking collagen supplements can help to reduce joint pain overall, rebuild cartilage in the joints and promote the tissues to produce higher levels of collagen within the body.
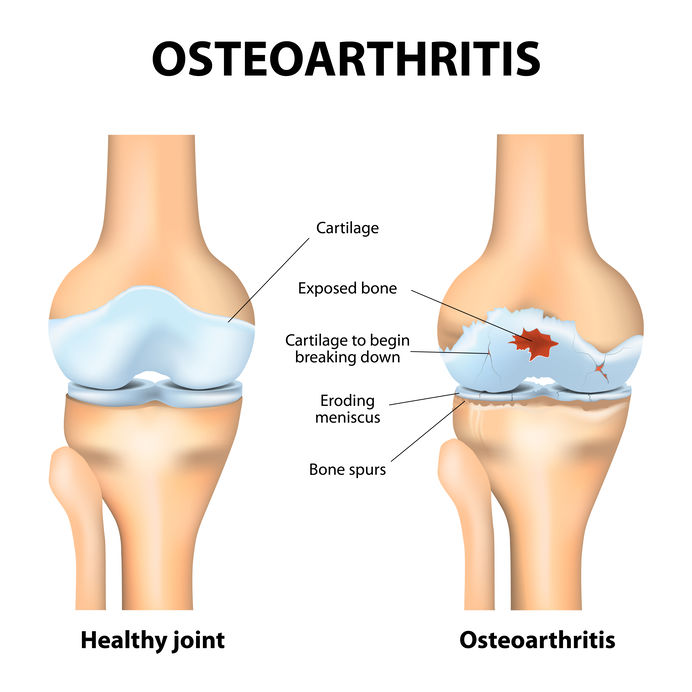
One study revealed that athletes who took 10 grams of collagen per day over the course of approximately 5 months did not experience such intense pain in the joints in comparison to those who were not taking the supplement. Another publication revealed that adults who ingested collagen supplements felt a significant reduction in joint pain and were able to perform physical activity better than those who were not taking the supplement.
Increases Muscle Mass
As we mentioned previously, the muscles are comprised of 1 to 10% of collagen. Many studies suggest that taking exogenous collagen can help boost muscle mass after exercise and encourage the synthesis of creatine (a muscle protein). Some researchers also found that collagen supplements help to build muscle mass in individuals who suffer from age-related muscle loss also known as sarcopenia.
Increases Bone Density
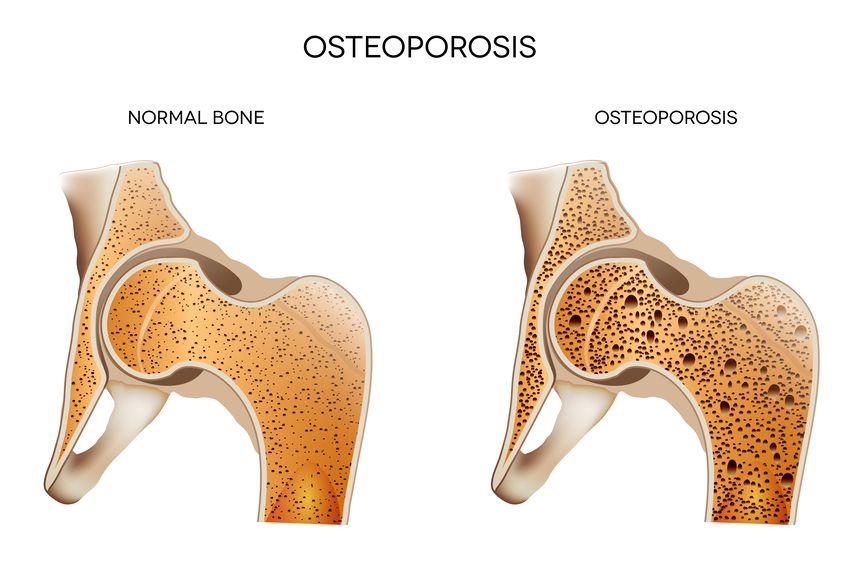
The age-related decline in collagen can increase the risk of developing osteoporosis, a low bone density disorder that is linked to bone fractures. Research has shown that taking hydrolyzed collagen can help to prevent bone mass from depleting. In one study, scientists found that women who had taken calcium and collagen supplements had lower levels of the specific protein that encourages the breakdown of bones compared to those participants who were taking a calcium supplement alone. Another publication revealed that women who had consumed exogenous collagen experienced an increase in bone mineral density (BMD) of approximately 7%.
Collagen peptides are especially beneficial for women who are experiencing menopause, which many researchers have discovered a strong link to developing osteoporosis.
How Do Keto Dieters Benefit From Collagen Peptides?

Collagen is beneficial for our overall health, but there are a few specific reasons why collagen is beneficial for keto dieters. Keto collagen is not only a convenient way to meet your protein requirements for the day, but it also helps to stave off some side effects of the keto flu. Here are a few ways keto dieters can benefit from taking collagen peptides.
Improves Digestion And Gut Health
One of the many reasons we experience the keto flu symptoms is because our bodies excrete more water and vital electrolytes during the transition into ketosis. Collagen peptides help to repair intestinal barrier cells. These barrier cells are important for circulation and play a role in enhancing the absorption of nutrients, water, and vital electrolytes. The barrier cells also prevent harmful microbes and pathogens from entering the body.
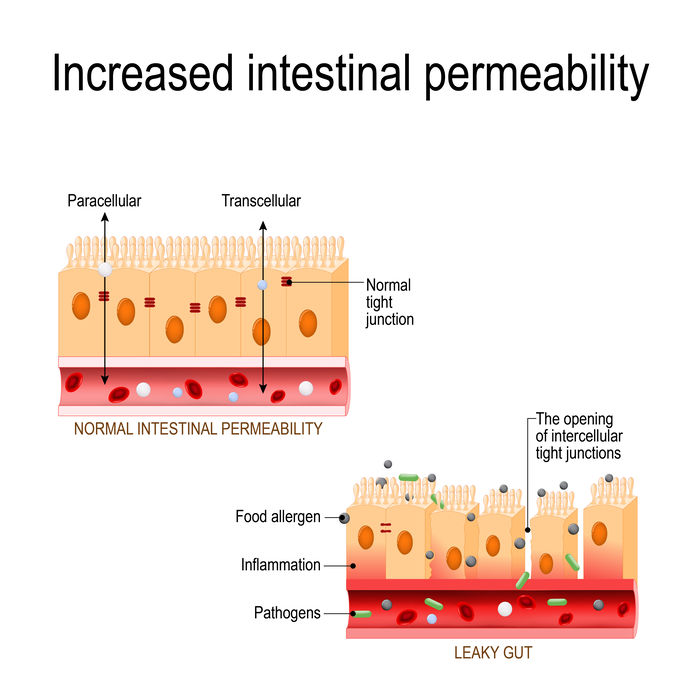
When the barrier is compromised, it can increase the risk of developing intestinal disorders such as leaky gut syndrome, diarrhea, celiac disease, and inflammatory bowel disease. Because of this, many nutritionists recommend eating more collagen-rich foods such as bone broth in order to restore the gut lining.
Many studies have shown that collagen peptides can help reduce fat accumulation, regulate lipid metabolism, and increase satiety. Some research suggests that taking collagen supplements at breakfast is more satiating than soy or whey proteins and can reduce the amount of food consumed throughout the day by almost 20%.
Promotes Sleep And Improves Mental Health
Struggling to fall asleep is one of the common side effects of the keto flu, but collagen can put this symptom to bed for good. Scientists suggest that the main amino acid found in collagen, glycine, can help improve the quality of sleep you get at night. Glycine can also improve cognitive function, increase REM, and decrease fatigue during the day.
Another amazing benefit of glycine is that it can help boost your mental health. Research suggests that glycine acts as a neurotransmitter that has inhibitory effects on symptoms of depression, obsessive-compulsive disorder, and schizophrenia.
Additional Support For Type 2 Diabetes
While the keto diet can help melt away the pounds, it is also used to help patients manage type 2 diabetes. Collagen peptides can be a helpful tool for keto dieters who suffer from diabetes and other metabolic disorders. Studies have revealed that the glycine in collagen helps to reduce glycated hemoglobin, which is a form of hemoglobin linked to monosaccharides like fructose, glucose, and galactose. Research has also found that glycine can help reduce oxidative damage and stress that triggered when type 2 diabetes and other metabolic disorders start to develop.
The Different Types Of Keto Collagen Supplements
There are a few different types of collagen peptides and choosing the right one for you can make all the difference when it comes to your health and the keto diet. The main collagen peptide sources are:
Bovine
This form of exogenous collagen is derived from the placenta, bones, tendons, cartilage, and hides of cows and other bovine animals. Although this may sound appealing to most, bovine collagen contains the three primary types of collagen and all the benefits we discussed earlier. Collagen type I, II, and III. this source of keto collagen can provide support to almost every tissue in the body and improve bone health. This is the easiest source of exogenous collagen to find, however, the quality of protein always depends on the health of the animal, which is why consumers should always opt for 100% grass-fed supplements.
Pig
Pig collagen is not the easiest type of exogenous collagen to source due to the quality and conditions most of these animals are kept in, however, if you do happen to find a good quality supplement, it makes a suitable alternative to bovine because it is the closest resemblance to human skin.
Chicken
While collagen from chicken is not as popular as bovine, it does contain the widest variety of collagen types. The reason why this source of hydrolyzed collagen is scarce is because of the risk it carries. Many chickens are at risk of contracting aviary diseases. If you have a sensitivity to bovine or just prefer chicken, it may be a safer option to make bone broth out chicken parts you don’t eat in order to reap the benefits.
Marine And Fish
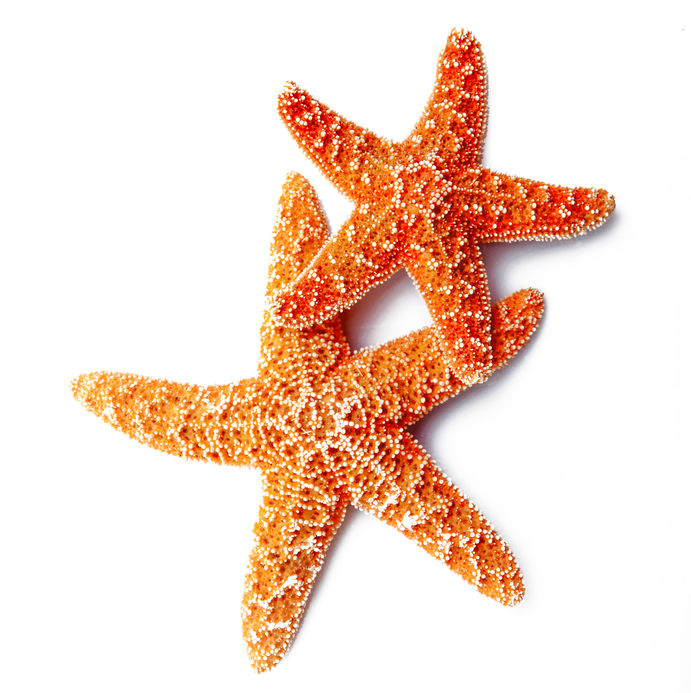

Marine collagen is derived from the tissues of different aquatic animals such as prawns, sea sponges, sea urchins, squid, and starfish. This source of exogenous collagen has many advantages because it is easier to absorb due to the smaller molecules and peptides and it is a more environmentally friendly process. Studies reveal that collagen derived from fish scales is so small that it is able to penetrate the epidermis and stimulate collagen production within the body much easier than many other sources.
Eggshell Membranes
Egg whites and shells contain collagen types I, III, IV, and X. Egg collagen also contains various amino acids, chondroitin sulfate, glucosamine sulfate, and hyaluronic acid, which makes it more effective than most other supplements when it comes to preserving and maintaining joint health.
Is There A Vegan Keto Collagen Alternative?
Thanks to brilliant scientists, collagen can also be made in a lab by using genetically modified yeast and bacteria, which is a great vegan-friendly alternative. Some studies have found that a specific strain of bacteria called P. pastoris is the most effective in genetically engineering high-quality exogenous collagen.
Vegan collagen is made by adding the four human genes responsible for coding collagen to the microbe structure. Once the genes have been added, the bacteria and yeast start developing the building blocks for human collagen. Pepsin, which is a digestive enzyme is then added to the molecules to give the building block structure and to help mimic the same structure of human collagen.
This process is also a more cost-effective way for consumers to get a higher quality form of exogenous collagen and reduces the risk for those who are allergic to eggs and other animal products.
How To Pick The Perfect Keto Collagen Supplement For You

Finding the perfect keto collagen can be a challenge, especially because the market is quite saturated with products. It can be difficult to distinguish which product contains high-quality ingredients and which are loaded with unnecessary fillers. The general rule of thumb is to look for products that are:
- Derived from sustainably-raised sources
- Free from fillers and binders
- Do not contain any preservatives
- Do not contain non-keto sweeteners or gelatin
- Only contain 100% natural ingredients
- Keto approved
- FDA certified
- Contain collagen I, II, and I
Some keto collagen supplements also contain sodium to help replace lost electrolytes.
Safety and Side Effects Of Collagen Peptides
Hydrolyzed collagen is a safe and effective way to supplement the body with the collagen it needs, however, it is always advisable to consult with your healthcare provider before taking any supplements, especially if you are allergic to fish, egg, or bovine.
There are not many known side effects of taking collagen peptides besides possible allergies to the animal and food sources listed above. Some have reported that collagen can cause digestive issues such as heartburn, but overall, hydrolyzed collagen appears to be safe for most individuals.
Our Final Word On Keto Collagen
Collagen plays a vital role in almost every tissue and structure in the body. It helps our bones, muscles, joints, nails, hair, and eyes to function properly and adding collagen peptides to a keto diet can have a positive impact on keto flu symptoms and digestion. While there are many sources of exogenous collagen peptides, it is important to look for products that adhere to quality and keto standards. Supplements that are sourced from sustainably raised sources and do not contain any unnecessary fillers are your best bet when it comes to purchasing these products. The added benefit of taking exogenous collagen supplements is that it is a safe, effective, and convenient way of reaping all the benefits that endogenous collagen offers.

