With the rising popularity of the keto diet, many health products have also been appearing on our radars. Products that we may have heard about before but never really understood what they are actually for and how they benefit us. One of these many products is MCT oil. We may have heard MCT oil being mentioned here and there or spotted the ingredient on a food label but what is it sourced from and how can we gain from using it? More importantly, how does it help us achieve keto success? If some of these questions are burning in your mind, here is everything you need to know about choosing the best MCT oil and how to use it to your advantage.
What is MCT Oil?

MCT is short for medium-chain triglycerides. Triglycerides are the technical term for fats which is why MCTs are also referred to as medium-chain fatty acids (MCFA). The reason why these triglycerides or fatty acids are called ‘medium’ chain is that they are comprised of 6 to 12 carbons atoms. Fatty acids are lipid molecules that contain a carboxylic acid group attached to one end of the chain and hydrogen and carbon atoms at the other end of the chain. These hydrocarbon chains vary in length depending on how many carbon atoms are in the chain, which can range from as little as 2 all the way up to 22. Long-chain fatty acids (LCT), which are the most predominant type of fat in the American diet comprises of 13 to 18 carbon atoms. MCT’s as we mentioned before range from 6 to 12 while short-chain fatty acids (SCT) have 6 or less carbon atoms in their structure.
How SCTs, MCTs, And LCTs Differ
The two main functions of triglycerides is to be used as fuel or stored as fat cells. How many chains each fatty acid contains may seem like futile information at first, but it is what sets each one apart in terms of digestion.
The keto diet focuses on high-fat consumption in order to create ketones, which are then burned for fuel as opposed to glucose. The easier a fatty acid is to digest, the quicker the body can use it for energy, which most keto beginners need in order to kick the sluggish feeling while transitioning into ketosis. The rapid absorption of a fatty acid also means that it is less likely to be stored as body fat.
Long Chain Triglycerides
Since long-chain triglycerides (LCTs) contain more carbon atoms than short or medium-chain triglycerides, it requires a lot more effort for the body to digest. In order for the body to absorb LCTs from fatty foods, it must also excrete bile, enzymes, and chylomicrons to break down these fatty acids first.
Once they are absorbed, they are transported to the lymphatic system first and then finally to the organs to be burned for energy or stored. There are currently 17 notable types of LCT, which include omega 3, 6, and 9 fatty acids, myristic acid, oleic acid, stearic acid, and erucic acid. Almost every type of fatty food contains long-chain triglycerides.
Short Chain Triglycerides
Unlike LCTs, the common source of short-chain fatty acids is not found in our diets but rather absorbed from the gut. The beneficial bacteria in our gut break down foods such as fiber to produce SCTs, which are then used to protect and nourish the cell lining in the colon and provide our body with nutrition and energy.
Small traces of short-chain fatty acids are also found in butter, cows milk, and cheese, but the majority of our short-chain fatty acid content is a byproduct of beneficial gut bacteria. Acetate, Propionate, and Butyrate make up roughly 95% of all short-chain fatty acids, which studies reveal are beneficial for regulating glycemic response, reducing inflammation, and improving intestinal health (1).
The best way to increase SCT intake is to eat more low carb vegetables that are high in fiber.
Medium Chain Triglycerides
MCTs are not metabolized in the same way as LCTs, which is exactly why they have become the star of the keto diet. Since the chains are shorter, the body does not require much effort to break down and absorb these triglycerides. Unlike LCTs, MCTs do not pass through the lymphatic system, instead, they are absorbed directly by the liver. The liver converts medium-chain fatty acids directly into energy and ketones. Another reason why MCTs are the perfect keto fat is because of its caloric content. They are converted into energy more efficiently than any other fatty acid and are less likely to be stored as body fat. Studies also reveal that MCTs provide the brain cells with a more efficient source of energy when compared to glucose (2). The study also suggests that MCTs may help block the onset of seizures and raise the seizure threshold through various mechanisms such as mitochondrial biogenesis. Since many epileptic patients use the keto diet to control seizures, incorporating the best brand of MCT oil like Approved Science® MCT Oil into your diet to help amplify positive results.
The Different Types Of MCTs And Where They Are Sourced From
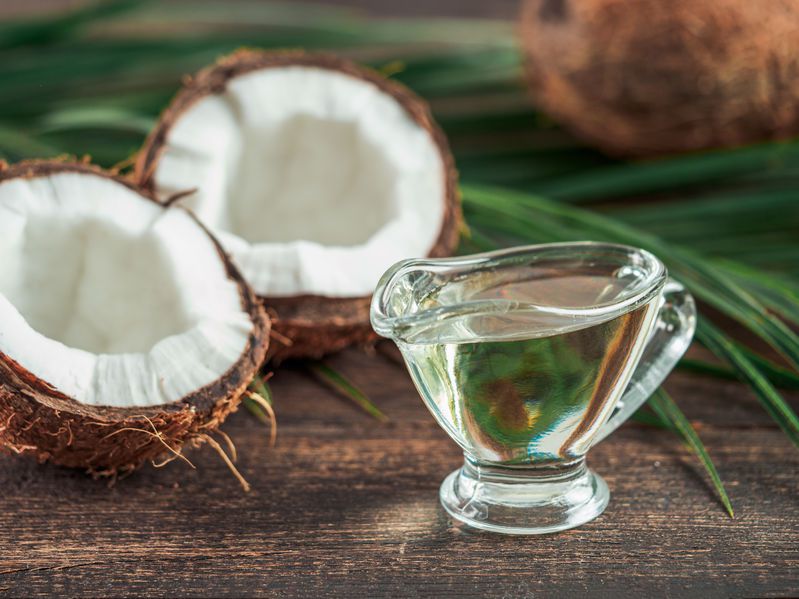

In order to choose the best quality MCT oil, it is worth knowing the different types of medium-chain triglycerides found in foods and supplements. MCTs are commonly sourced from both plant and animal products but there are a few specific foods that contain the highest concentration of MCTs. These include:
- Coconut oil, which is comprised of more than 60% of medium-chain fatty acids.
- Palm kernel oil, which is comprised of more than 50% of medium-chain fatty acids.
- Dairy products including breast and cow’s milk are comprised of about 10 to 12% of medium-chain fatty acids.
There are four types of medium-chain triglycerides that are naturally sourced from these foods.
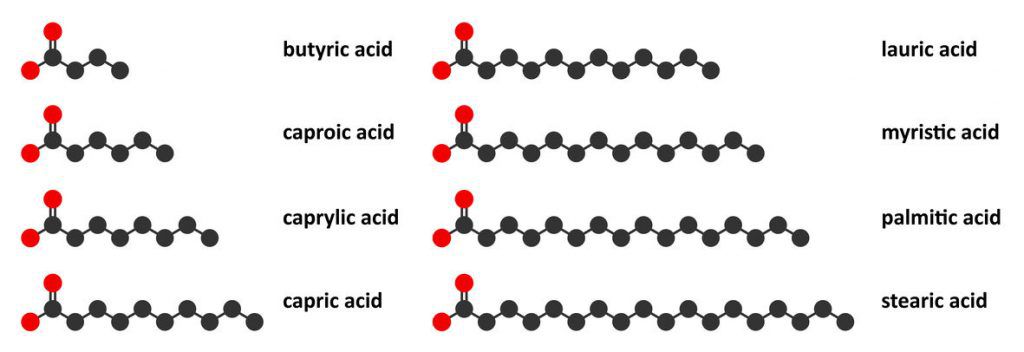
- Caproic Acid, which contains 6 carbon atoms (C6)
- Caprylic Acid, which contains 8 carbon atoms (C8)
- Capric Acid, which contains 10 carbon atoms (C10)
- Lauric Acid, which contains 12 carbon atoms (C12)
Caproic Acid
This type of MCT has the least amount of carbon atoms, which means that it is broken down and converted into ketones a lot quicker than the other types of MCTs.
The only downside is that caproic acid does not have a very pleasant taste and tends to cause a mild tingling sensation in the throat after ingestion.
Caprylic Acid
Caprylic acid is the most prevalent form of MCT found in most MCT oils. While it may have two more carbon atoms than caproic acid, it is still absorbed and used for energy quickly. Studies have suggested that caprylic acid may show promise in reducing symptoms associated with candida infections, upper respiratory problems, incontinence, and tooth infections (3). When choosing the best MCT oil look for a higher concentration of caprylic acid or C8 in the ingredients.
Capric Acid
Another prevalent type of MCT found in MCT oil is capric acid. Much like C6 and C8, capric acid is also absorbed directly from the liver and converted into ketones for energy. It does have a longer chain structure than the ones mentioned above, so it is processed a bit slower, but it is still quick enough to prevent the body from storing it as fat.
Lauric Acid
There is some debate around whether lauric acid should be classified as an MCT due to its carbon atom content. Lauric acid acts similarly to long-chain triglycerides because of the time it takes the body to fully digest and utilize it. Lauric acid also causes cholesterol levels to rise, which is why most good quality MCT oils do not include lauric acid in the formula.
Each of the natural food sources mentioned above contains varying amounts of these four types of MCTs, but when choosing the best MCT oil for your needs, it all boils down to which type of MCTs have been extracted and added to the formula.
How Is MCT Oil Made?
MCT oil is made via a complex process known as fractionation, which involves heating natural oils beyond their melting point and cooling them back down to solidify. This process is used to separate the naturally occurring medium-chain fatty acids from palm kernel or coconut oil. Once the MCTs have been extracted from the palm or coconut oil, lauric acid, and caproic acid are removed from the final product to make it a more absorbent and palatable product. Generally, the best MCT oils contain a concentration of caprylic acid (C8) normally around 50 to 80% as well as a concentration of capric acid (C10) around 20 to 50%.
How Does Taking The Best MCT Oil Benefit Your Health?
MCT oil benefits go beyond the keto diet and weight loss. In fact, in the 1980s, a researcher by the name of Dr. Vigen K. Babayan developed the process of extracting large quantities of MCTs with the intention of addressing various medical conditions such as hyperchylomicronemia, pancreatic insufficiency, and fat malabsorption (4). Thanks to some of these revelations, there has been a multitude of studies done on the benefits of MCT oil and the outcomes are promising. Here are a few ways a high-quality MCT oil can benefit you:
Antifungal Effects
As we touched on before, caprylic acid has powerful antifungal effects against candida infections. An overgrowth of candida Albicans is usually responsible for vaginal yeast, oral thrush, and nail infections. The antibacterial and antimicrobial properties of caprylic acid are also beneficial for fighting against bacterial skin infections such as dermatophilosis. According to scientists, capric acid is also effective in fighting infections because it is able to break down candida cell membranes (5).
Heart Health
MCT oil is continuously undergoing various studies in order to determine its maximum potential. Possibly one of the most intriguing benefit MCT oil has to offer is that it can help improve the metabolism of cholesterol and reduce the risk of atherosclerosis, which is the buildup of plaque in the arteries.
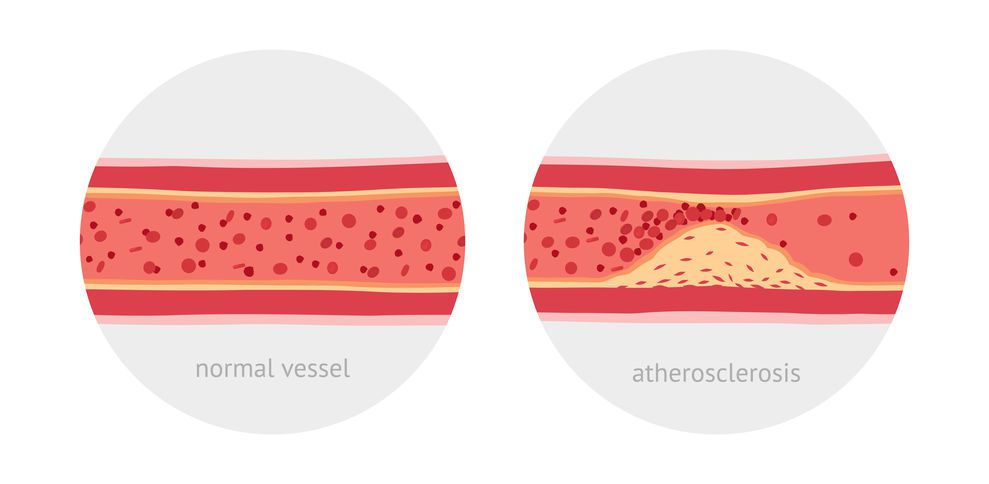
Studies have found that mice who had been fed medium-chain triglycerides showed a decrease in atherosclerotic plaques and body fat mass and an improvement in serum lipid profiles (used to measure cardiovascular risk) (6).
Another human study conducted on overweight men showed that taking a combination of MCT oil, flaxseed oil, and phytosterols for a period of 29 days reduced cholesterol levels by 12.5% in comparison to those who had used olive oil and only showed a reduction of 4.7% (7).
Promotes Weight Loss
The best MCT oils like Approved Science® MCT Oil combat weight loss in more than one way. Studies conducted on MCT oil show that they increase the release of two hormones that encourage satiety (8). These hormones are known as leptin and peptide YY.
Leptin, also referred to as the ‘starvation hormone’ plays a crucial role in signaling the brain that there are enough fat stores in the body and it does not require more food. The main function of this hormone is to keep us from overeating or starving by regulating the number of calories we burn, how much we eat, and how much fat is stored in the body.
Much like leptin, peptide YY also helps to encourage satiety and enhance fullness but in a different way. Peptide YY is excreted by the pancreas, which is then released in the bloodstream. Once it reaches the brain, it binds to receptors in the brain, resulting in an anorectic effect or in other words reduces the appetite. Peptide YY also inhibits gastric motility meaning that it helps to slow down digestion, which keeps us feeling fuller for longer.
As we mentioned before, the body metabolizes MCTs differently. The body is able to use MCT oil as an almost instant source of energy instead of storing it. Scientists have revealed that MCT oil significantly reduces both waist circumference and body weight (9).
Protects Against Cognitive Issues
MCT oil helps to promote ketosis and helps to generate ketones. Ketones are not only beneficial for losing weight but also provide the brain with a more efficient source of fuel compared to glucose. Ketones have an incredible effect on the brain and according to studies may help boost cognitive function in those who suffer from mild Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and dementia (10).
Choosing The Best MCT Oil

With so many brands and manufacturers to choose from, it can be difficult to decide on the best MCT oil for you. There are many factors to consider when making a decision. You don’t want to spend hard-earned money on a product that does not deliver any results after all. But how can you tell which product contains the highest quality medium chain triglycerides? It simple, arrow down your search by looking for tried and tested brands. Ones that have enough data and studies to back up their claims. Here are a few things to look for in an MCT oil:
Evaluate The Manufacturer

Before adding the product to the cart, do a bit of research on the manufacturer. Look for reviews, links to clinical studies on the website, and a GMP certification. Another company standard to look for is a money-back guarantee. Companies who are confident enough to give you your money back show that they have confidence in their products and value their customers. Other key things to look for are if the product has an animal cruelty free and vegan approved seal.
Ingredients
Usually, the best MCT oil formulas contain two out of the four medium-chain triglycerides, which are caprylic and capric acids. As we discussed, these MCTs are easy to digest and won’t be stored as fat. Avoid products that contain lauric acid and caproic acid as this will leave a bad taste and won’t be digested or converted into energy as efficiently.
Avoid Powdered MCT Oil
Some MCT oil is available in powder form, which may be convenient when it comes to traveling, however, it comes with a hefty price tag. To make MCT oil into a powder, the moisture from the liquid is evaporated using heat and then bound to a carrier powder. Some manufacturers use different carrier powders such as acacia fiber. While the carrier powders are not harmful, they do have an effect on the potency of the product and contain a few more calories than the oil formula. Another downside to using powdered MCT is that it has not been researched as well as MCT oil. Without much evidence to back up MCTs in a powdered formula, the product is not guaranteed to deliver any results.
Fortunately, you don’t need to look very far to find a product that ticks all of these boxes. Approved Science® MCT Oil meets every criteria. It is made from 100% pure MCT oil (caprylic and capric acids), does not have any fillers or binders, is completely vegan-friendly and animal cruelty-free, and comes with an impressive money-back guarantee to put your mind at ease. The GMP Certification guarantees a safe, high potency quality formula in every bottle.
How Much MCT Oil Should You Use?
While using MCT oil is the best way to get a quick boost of energy on the keto diet, it is important to know that when taken in excess it can cause some gastric discomfort. The side effects are by no means harmful, but if you take too much, it can cause stomach cramps or nausea.
It’s always best to stick to 1ml or about 20 drops twice a day. This can be added to your coffee, salads, smoothies, or drizzled over a decadent fat bomb. MCT oil has a very low smoke point so it’s not intended for high heat cooking or baking.
The Best MCT Oil – The Takeaway
MCTs are the new chains on the block that have sparked interest in both scientists and the weight loss community. Countless publications have found MCT oil to be greatly beneficial to our overall health, and the evidence is just getting stronger day by day. From weight loss to seizure relief, these fatty acids are addressing some of the issues that affect our quality of life. By adding a good quality MCT oil to your diet, you will reap some of the incredible heart and cognitive boosting properties these little chains have to offer.

